
Unlocking the potential of Industry 4.0
Unlocking the potential of Industry 4.0
"In a smart factory constellation, we examine the devices on component level as well as system level. Subsequently, risk can be reduced while tapping the full potential of smart factory technologies. Combining human creativity, problem solving and experience with innovative safety assessment tools, TÜV SÜD is ready for a smart future"
Dr. Detlev Richter
Global Head of Industrial and Energy Products at TÜV SÜD
Friday, June 23, 2017
Set to revolutionise our lives, the fourth industrial revolution is upon us, promising substantial improvements in efficiency, quality and flexibility. Standing on the threshold of Industrie 4.0, what is required to reach maturity and reap the full benefits of smart manufacturing?
The ongoing digital transformation is driving innovation across a wide range of areas such as agriculture, energy, transportation and healthcare. Industrial manufacturing will face massive disruption as development moves towards fully connected, self-organising intelligent factories.
This will trigger significant potential for efficiency improvements, for instance by reducing energy consumption and preventing downtime. Furthermore, industries can utilise smart components to improve asset and supply chain management, enhance quality, and shorten time to market.
Advanced new sensors are already finding their way into modern manufacturing lines, facilitating informed decision-making. But this is just the beginning.
Today’s manufacturing lines are based on informed decision-making by humans.
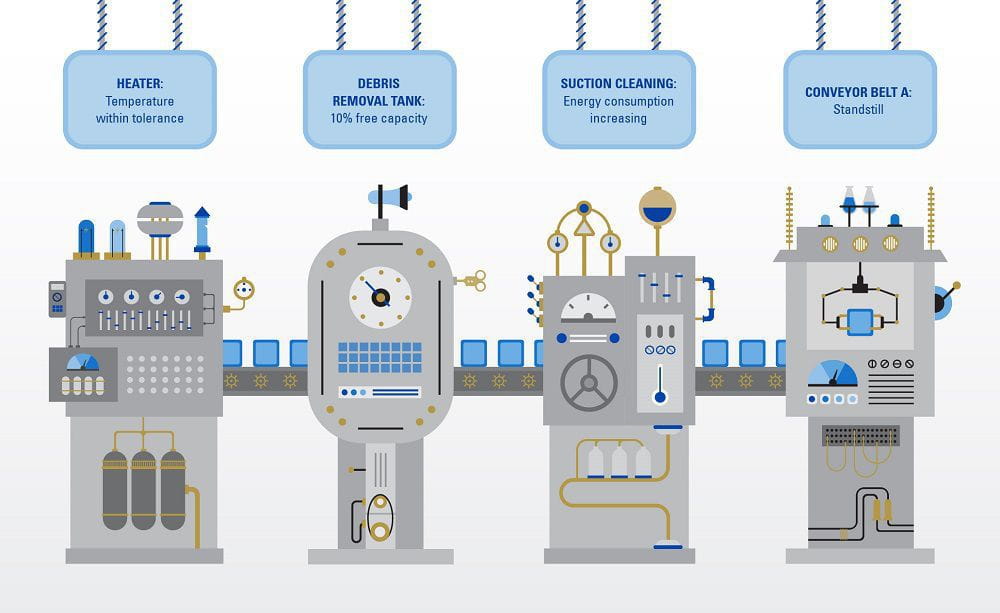
By combining the strengths of the physical and virtual worlds, cyber-physical systems have the potential to significantly enhance industry performance, facilitate new products and spark innovative business models.
In the longer term, advances in autonomy and flexibility will drive a shift in the economic principles of production. For example, it will be possible to manufacture small lot sizes cost-efficiently, meeting an increasing demand for customised products.
In the Industry 4.0 factory, manufacturing devices will autonomously self-optimise.
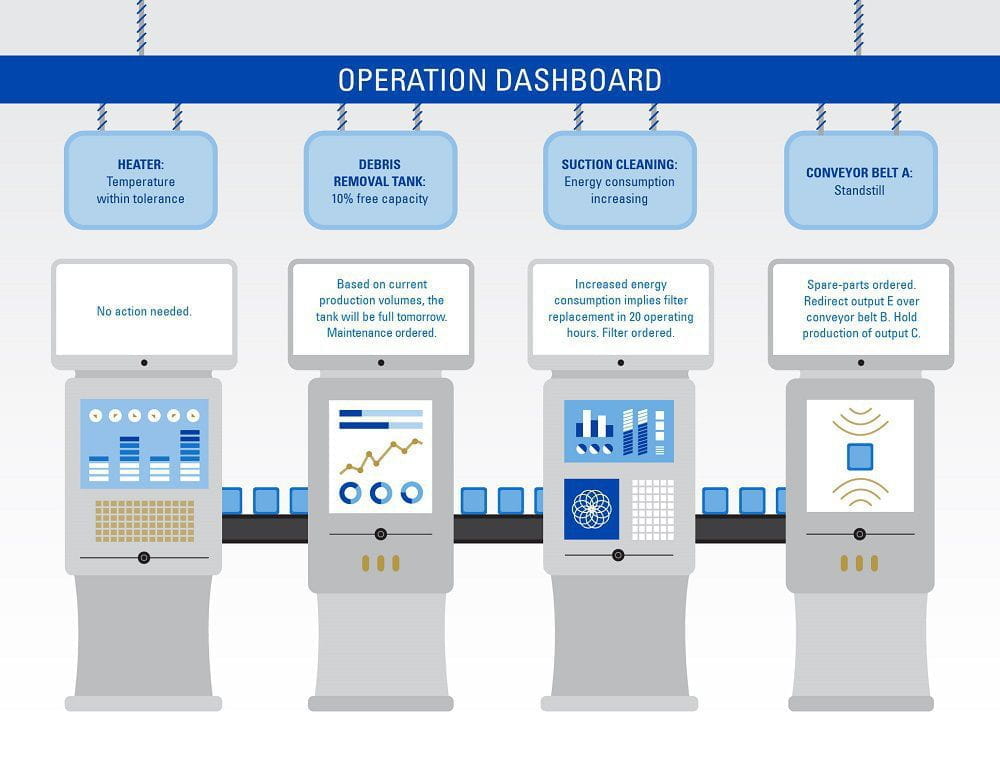
However, in order to unlock the full potential of smart component technologies, further innovations are required.
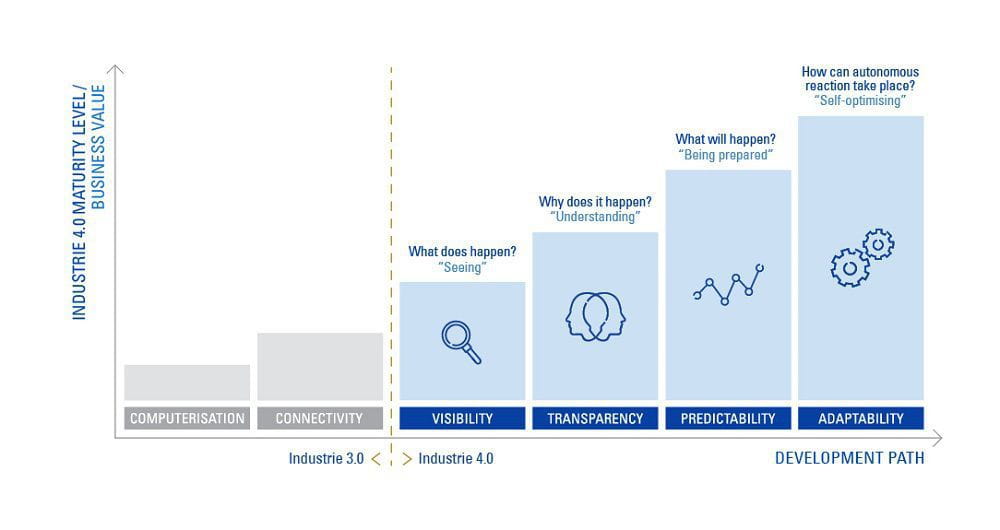
Milestones on the road to Industry 4.0 include component attributes such as visibility, transparency, predictability and adaptability. It’s important to note that each development step represents a discrete business value, and that companies can profit from a stepwise implementation approach as technology advances.
Technology roadmap towards smart manufacturing. Source: RWTH Aachen Campus, Cluster Smart Logistik
The completion of the technology roadmap as illustrated above would imply that smart components have the ability to interpret their environment and autonomously react to it. At this stage, smart components could theoretically be combined to form a mature smart factory in the vision of Industry 4.0.
Technology roadmap towards smart manufacturing. Source: RWTH Aachen Campus, Cluster Smart Logistik
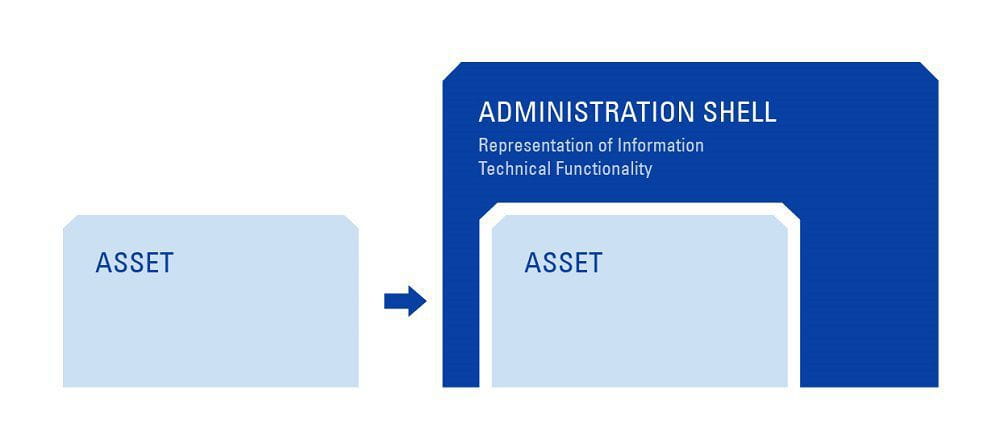
However, each manufacturing device enters the production line with its set of proprietary interfaces. In other words, the components each speak a different language. How can we facilitate smooth and dynamic interoperability among odd components? The solution is an electronic reproduction – a so-called “digital twin” or “administration shell” – of each physical component. The digital twin contains the complete set of parameters of its physical sibling, as well as adaptive algorithms for decentralised self-optimisation and safety measures. Acting as an intermediary, the digital twin functions as a standardised interface between the smart components, facilitating flawless interoperability.
Paired with an administration shell, the manufacturing asset is transformed into a smart component, also known as an I4.0 component. Source: DIN SPEC 91345:2016-04
As we stand on the threshold of Industry 4.0, what mindset is required today to ensure that organisations can reap the full rewards in time?
It’s vital to consider the shifting landscape of risk. A smart factory will see reduced risk in several areas, such as fewer worker injuries as machines take over hazardous tasks. But the increasing number of physical and digital interfaces also introduces vulnerabilities. With interconnected devices controlled by intelligent dashboards, new risk and liability issues arise. Based on its complexity, a dynamically reconfigurable system requires an integrated approach to safety assessment.
To facilitate the implementation of Industry 4.0, TÜV SÜD experts are developing a modular certification scheme for smart factory components. The methodology is currently being verified in the framework of the demonstration project SmartFactoryKL in Kaiserslautern, Germany. The pilot project addresses issues such as interface standards, interoperability, functional safety and IT security. The safety and security methodology represents the final crucial requirement necessary to realise the vision of tomorrow’s smart factory.
Sélectionnez votre emplacement
Global
Americas
Asia
Europe
Middle East and Africa